France 2019: economic outlook, potential growth, structural reforms and long term challenges
- French economic profile, May 2019
02/05/2019
After a strong acceleration in 2017, a combination of global and local factors led to a deceleration of economic activity in France in 2018 which could continue in 2019. France’s potential growth remains weak in part because of a rigid labor market and depressing productivity. The government has implemented reforms (capital taxation, labor market) to address France’s structural economic issues, particularly its weak fiscal position and lack of competitiveness. A reform of the retirement system is also planned but its enforcement will probably not be easy in a tense political context.

I. French economic climate : key figures and trends
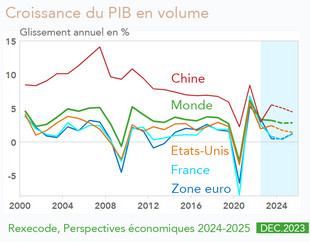
- The recovery fell out of breath.
- A stagnation in purchasing power per household since the onset of the 2008-09 crisis
- The level of inequalities in France
- Outlook for the French economy
II. Structural economic situation : a potential growth a little above 1%
- A relatively low inclusivity on the labour market.
- The less educated are increasingly excluded from employment.
- The slow decrease of unemployment
- France’s attractiveness
- Conclusion: potential growth is expected to stabilize at its lowest in 10 years
III. Long-standing challenges
Challenge 1 : Public finance sustainability
- The sustainability of public finances in France
- The level and quality of public finances
- The level and quality of government expenditures
- The level and quality of government revenues
Challenge n°2 : regain competitiveness
IV. Structural reforms: what has been done? What are the next steps to raise potential growth in the medium run?
- The taxation of capital : a paradigm shift that favours growth
- An ambiguous policy on labour taxation. 35
- Measures targeting the labour market : seeking a better fit with the current climate
- Retirement reform
- The government is planning an important, structural reform of the retirement system
- The current and projected performance of the retirement system
- The implications for policy recommendations